Bone Supported Anterosuperior Boundary of the Oral Cavity
Rea between the teeth and lipscheeks wormlike sac that outpockets from the cecum initiates protein digestion structure attached to the lesser curvature of the stomach organ distal to the stomach valve controlling food movement from the stomach into the duodenum posterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity location of the hepatopancreatic. Bone-supported anterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity.
Bone-supported anterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity List B a.

. Posterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity __A__ 22. Bone-supported anterosuperior boundary of oral. Posterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity.
Region containing two sphincters through which feces are expelled from the body. Anterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity. Hardest substance in the body.
Bone supported anterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity Haustra pocket like structure in the large intestine Ileocecal valve valve at the junction of the large and small intestine Large Intestine absorbs water and forms feces Lesser omentum structure attached to the lesser curvature of the stomach Mesentery. Bone-supported anterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity. The general anatomical features of the alimentary canal are listed below.
Use the key to identify each tooth area described below. Region containing two sphincters through which feces are expelled from the body __G__ 23. Hardest substance in the body Enamel.
Visible portion of the tooth b 2. Region containing two sphincters through which feces are expelled from the body. Visible portion of the tooth in situ Clinical Crown.
Fill in the table to complete the information. Visible portion of tooth in situ. Material covering the tooth root Cementum.
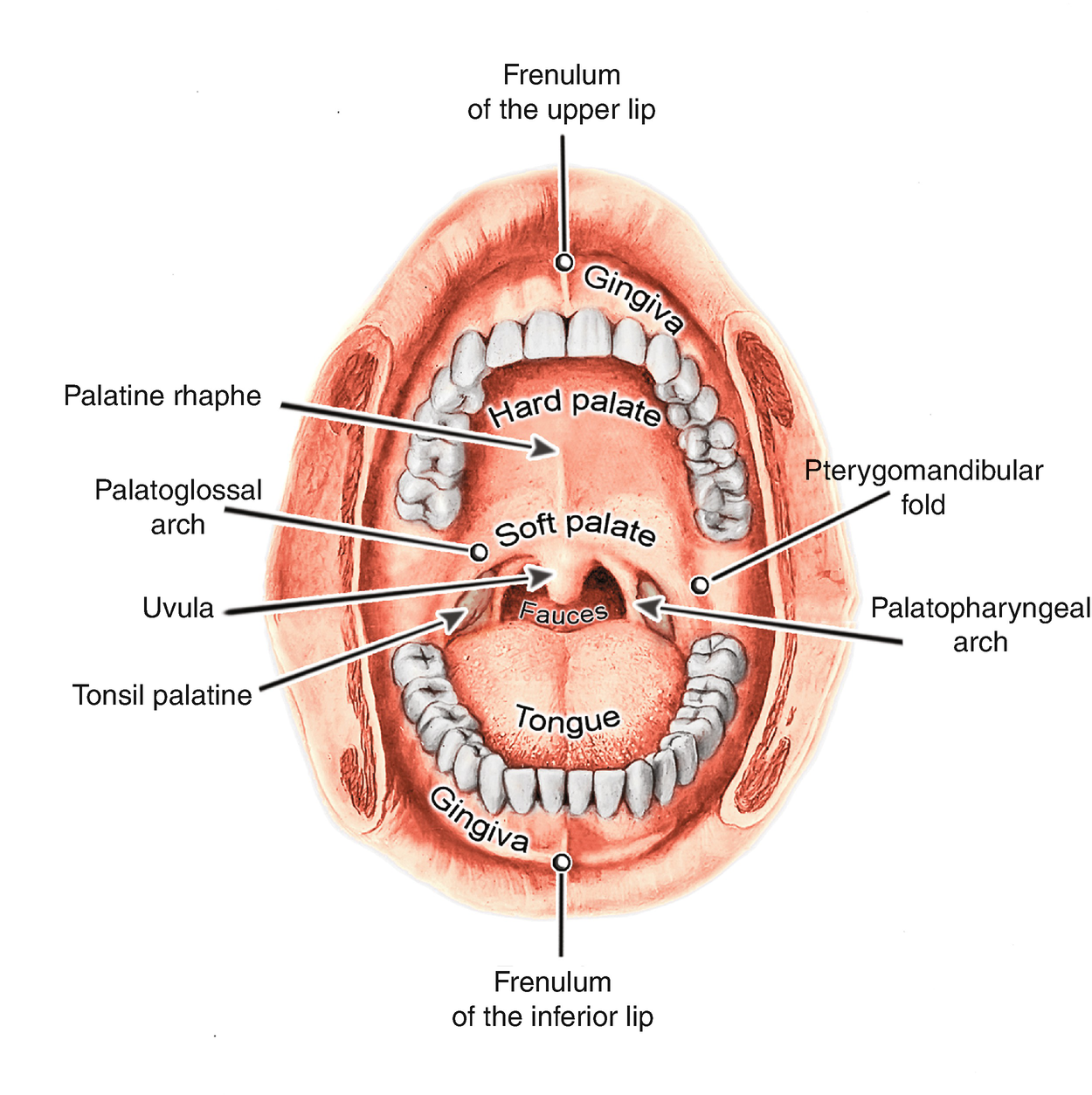
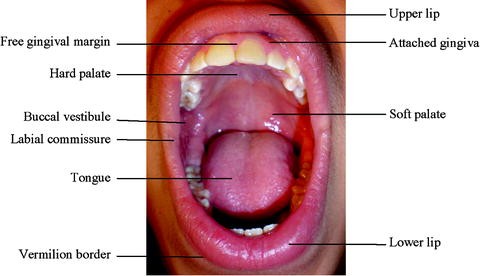
Material covering the tooth root. 112 rows Bone-supported anterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity Hard Palate. Material covering tooth.
Pyloric valve 19 posterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity soft palate 20 region containing two sphincters through which feces are expelled from the body anus 21 bone-supported anterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity hard palate 22 Pocketlike sacs of the large intestine haustra 23 Covers the most of the abdominal organs like an apron. Wall layer Subdivisions of the layer if applicable Major functions mucosa uni00A0 uni00A0 submucosa uni00A0 uni00A0 muscularis externa uni00A0 uni00A0 serosa or adventitia uni00A0 uni00A0 Organs of the Alimentary Canal 2. Serious membrane forming part of the wall of the small intestine.
Valve at the junction of the small and large intestine. Structure attached to the lesser curvature of the stomach small intestine F 19 covers most of the abdominal organs like an apron soft pilate 20. Wive controling food movement from the stomach into the duodenum stomach f -_21 posterssuperior boundary of the oral cavity torput 1 22.
Anteriosuperior boundary of the oral cavity supported by bone. The bony part of the roof of the mouth anterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity. Bone supported anterosuperior boundary of oral cavity anus region containing sphincter through which feces are expelled from body large intestine principle site for synthesis of vitamin k by Microorganisms parietal peritoneum Serous lining of abdominal cavity wall small intestine.
Visible portion of tooth. Rea between the teeth and lipscheeks wormlike sac that outpockets from the cecum initiates protein digestion structure attached to the lesser curvature of the stomach organ distal to the stomach valve controlling food movement from the stomach into the duodenum posterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity location of the hepatopancreatic. Serous lining of abdominal cavity wall.
Location of hepatopancreatic sphincter through which pancreatic secretions V tongue and bile pass 23. Pocketlike sacs of the large intestine. Region containing 2 sphincters through which feces are expelled from body.
Principal site for synthesis of Vit K by microorganisms. Region containing two sphincters through which feces are. Serosa of the abdominal cavity wall.
Material covering the tooth root e 3. What is the anterosuperior boundary of the oral cavity that is. Supported by bone formed by the palatine and maxillary bones forms the floor of the nasal cavity and separates the oral and nasal cavities.
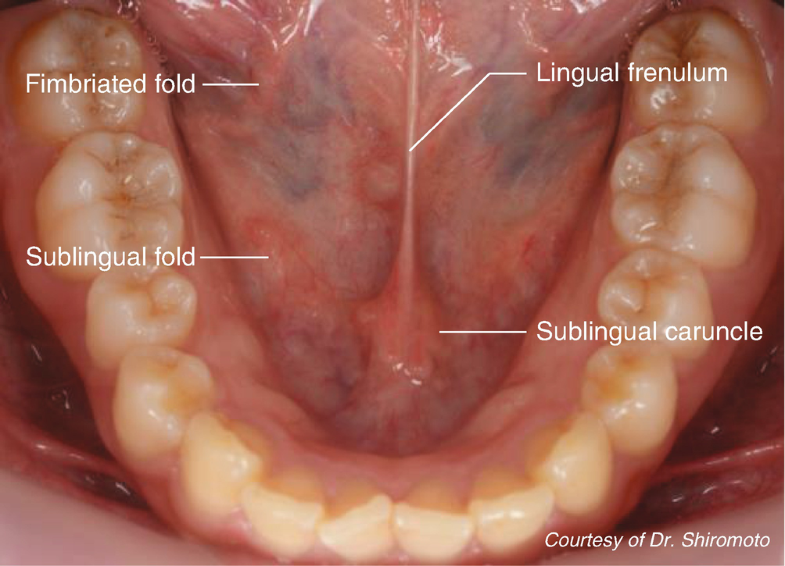
Membrane securing the tongue to the floor of the mouth. Posterosuperior boundary of oral cavity U stomach 22. Bone-supported anterosuperior boundary of oral cavity.
Region containing 2 sphincters through which feces are expelled X. Right to left - enamel - dentin - pulp cavity - gingiva - periodontal ligament - bone - cementum - root canal - blood vessels and nerves in pulp - root - neck - crown 10. Portion of the tooth embedded in bone root.
Attaches the tooth to bone and surrounding alveolar structures peridontal ligament. Serous lining of abdominal cavity wall W. Covers most of the abdominal wall like an apron.
Hardest substance in the body 11.
Anatomy For Usg Application In Head And Neck Springerlink

Solved Soft Palate V Stomach W Tongue X Villi Y Wnd Chegg Com
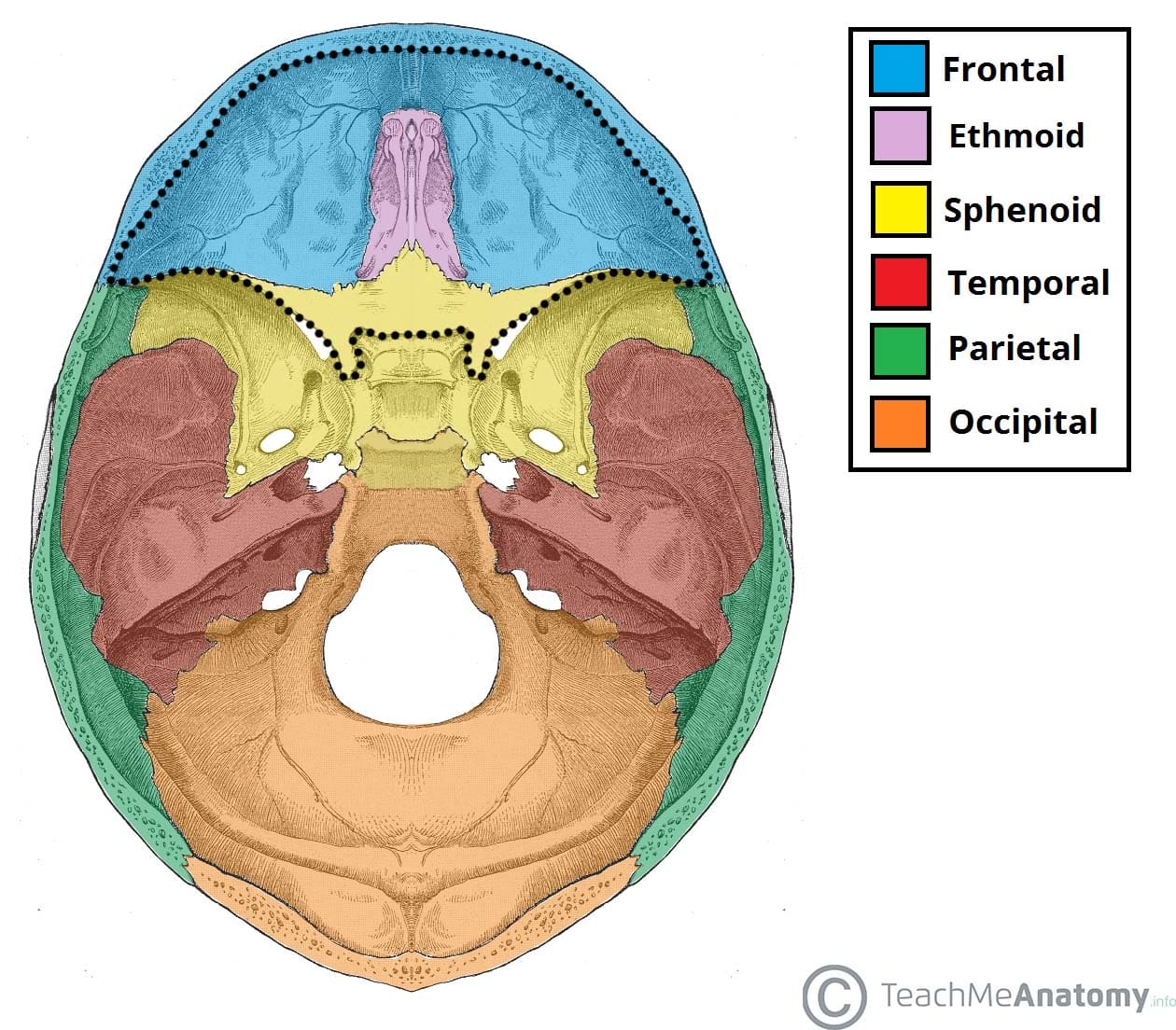
Anterior Cranial Fossa Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
Anatomy Of The Oral Cavity Springerlink

Anatomy Quiz 4 Flashcards Quizlet
Head And Neck Anatomy Springerlink

Floor Of Mouth The Term Floor Of The Mouth Is Used Differently By Different Authors But In All Cases It Is App Medical Anatomy Anatomy Images Muscle Anatomy
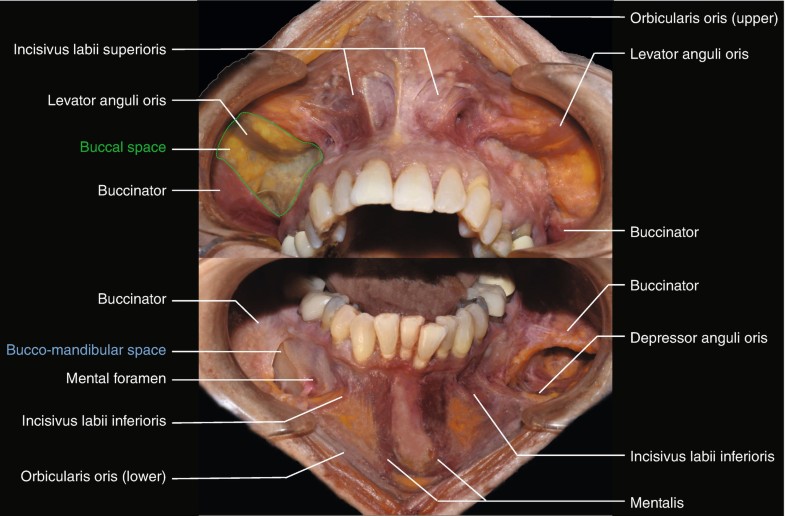
Anatomy Of The Oral Cavity Springerlink

Physician Assistant Pa 2013 Session 1 Tsai Flashcards An3 07 Nasal Cavity Parasinuses And Naso Nasal Cavity Human Anatomy And Physiology Medicine Notes

Bio 207l Faulk Exercise 38 Anatomy Of The Digestive System Flashcards Quizlet

Lecture 2 Embryology Of The Face And Oral Cavity Part 2 Flashcards Quizlet

Bones Of The Human Skull With Emphasis On The Sphenoid Temporal Maxilla And Mandible Bones Pocket Dentistry
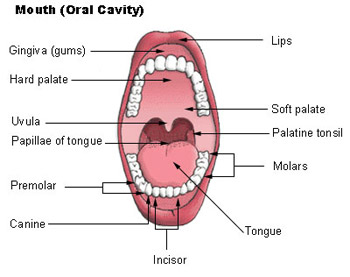
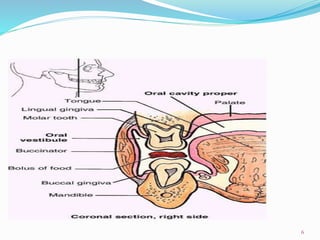
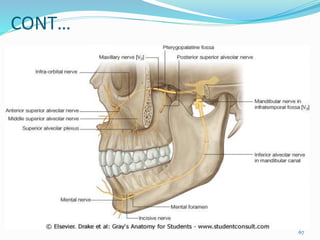
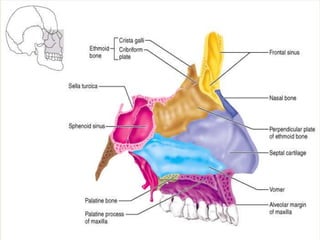
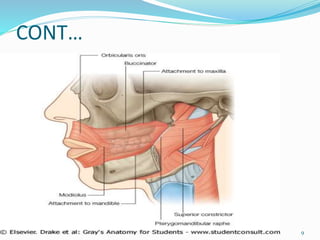

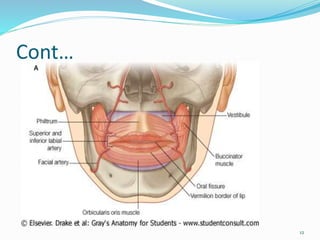
Comments
Post a Comment